Laparoscopic Surgery
In our efforts to provide the highest standard in medical care for your pets, we are thrilled to announce the addition of laparoscopic surgery at Concord Animal Hospital.
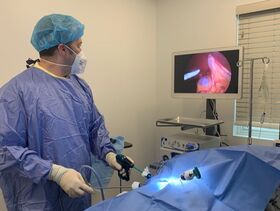
What is Laparoscopy?
In a laparoscopic procedure, a surgeon makes two-to-three small incisions. They insert a tube through each opening, and the camera and surgical instruments go through those. They look at a video monitor to see what is happening inside your pet and perform the operation. This minimizes tissue trauma, decreases pain, and speeds patient recovery.
What are the benefits of a laparoscopic procedure?
In a laparoscopic procedure, a surgeon makes two-to-three small incisions. They insert a tube through each opening, and the camera and surgical instruments go through those. They look at a video monitor to see what is happening inside your pet and perform the operation. This minimizes tissue trauma, decreases pain, and speeds patient recovery.
What are the benefits of a laparoscopic procedure?
- Faster and safer: improved visualization and magnification for the surgeon increases operative precision, reduces blood loss and tissue handling, and often results in a shorter procedure.
- Lower risk of infection: smaller surgical incisions reduce the risk of infection.
- Less pain: less tissue handling means a faster recovery and less trauma for pet patients.
- Faster recovery: activity restriction is recommended for the first 2-3 days after a laparoscopic procedure versus 7-14 days for most traditional surgical procedures.
 Petal three days after her LOVE Spay
Petal three days after her LOVE Spay
Is laparoscopic the right surgical option for my pet?
Your veterinarian may recommend a laparoscopic procedure for one of the following procedures where the surgeon needs access to the interior of the body cavity:
Your veterinarian may recommend a laparoscopic procedure for one of the following procedures where the surgeon needs access to the interior of the body cavity:
- LOVE Spay (short for a laparoscopic ovariectomy): a safer spay alternative for large breed dogs, pets that have gone through a heat cycle, or obese pets.
- Cryptorchid neuter: male pets with testes that are retained in the abdomen.
- Prophylactic gastropexy: securing the stomach to the abdominal wall to prevent stomach twisting.
- Liver biopsy
